Keloids are raised scars that extend beyond the original wound, posing a mystery to researchers. Despite the unclear exact cause, various factors contribute to their development. This article delves into the elements that make someone prone to keloids, shedding light on the complex nature of this skin condition.
Genetics
Genetics significantly influences keloid development. Those with a family history or specific ethnic backgrounds, especially those with darker skin tones, are more susceptible to keloid formation.
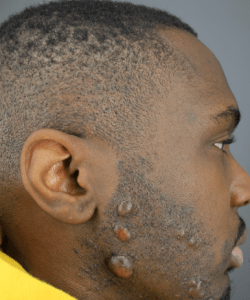
Skin Color
Keloid likelihood is influenced by skin pigmentation. Darker skin is more prone to keloids, and the location of the wound matters. Areas with less fatty tissue, like the chest, shoulders, and earlobes, are more predisposed.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as acne and chickenpox, increase the risk of keloid development. Surgeries, particularly on the chest, shoulders, or earlobes, can also heighten the likelihood. Individuals with a keloid history should inform healthcare providers before undergoing surgery.
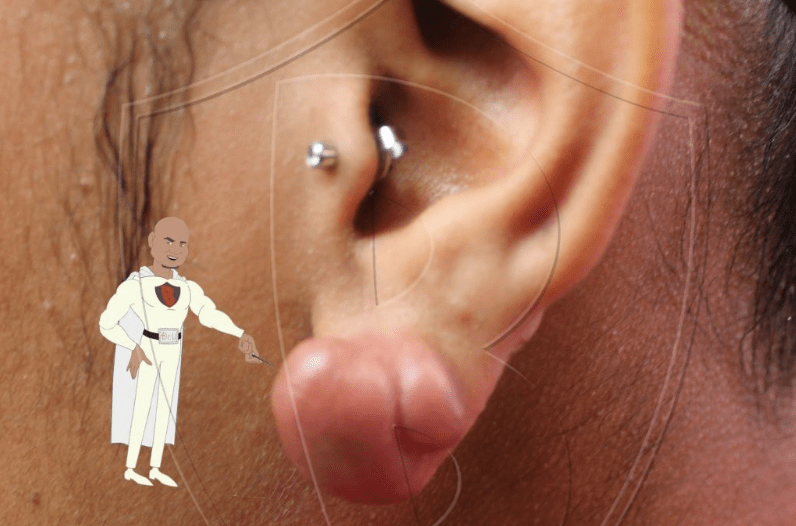
Vaccination Sites
Surprisingly, vaccination sites can become prime locations for keloids in individuals who have keloid predisposition. It’s crucial for those predisposed to discuss this risk with healthcare providers for alternative vaccination strategies.
Age, Immune System, and Hormonal Balance
Research suggests that age, immune system function, and hormonal balance contribute to keloid development. Younger individuals are more prone, and hormonal fluctuations during puberty or pregnancy may increase susceptibility. A compromised immune system can affect scarring regulation, potentially leading to keloids.
Conclusion
While the exact cause of keloids remains elusive, understanding the contributing factors is crucial. Genetic predisposition, ethnicity, skin color, wound location, medical conditions, surgeries, vaccination sites, age, immune system function, and hormonal balance collectively shape the complex nature of keloid formation.
Recognizing these factors empowers individuals and healthcare providers to take proactive measures in managing and mitigating keloid risks for better skin health.
Dr. Bumpinator, AKA Los Angeles board-certified dermatologist Dr. Sanusi Umar MD (Dr.U), advises individuals with keloid growth to seek guidance from a medical professional.